The BOK “must increase jobs by moving labor between high value-added industries and sectors”
It is analyzed that the real wage and the increase rate of workers are lowering as robots are rapidly spreading to the Korean industry, mainly in automobiles.
According to the report “The Impact of Industrial Robots on Employment” released by the Bank of Korea on the 27th, the number of industrial robots operated in Korea increased from 38,000 in 2000 to about 8 times in 2018 to 300,000 (based on the International Robot Federation).
The number of units sold has also increased from 50 million units to 38,000 units, which is approximately seven times.
During the same period, the total number of industrial robots operated and sold in the world increased 3.2 times (750,000 → 2439,000 units) and 4.3 times (99,000 units → 422,000 units), respectively, which is significantly faster.
The density of robots in Korea (the number of robots operated per 1,000 manufacturing workers), which was at an annual average of 1.26 units from 2000 to 2007, also jumped to 5.28 units a year from 2010 to 2018.
During the same period, Japan (0.07→0.12), the United States (0.9→0.93), Germany (1.09→0.89), and Taiwan (0.68→1.5) showed a larger increase.
The BOK analyzed that the rapid spread of industrial robots in Korea was due to the fact that the world robot price fell by 38.6% from 2009 to 2018, and the large proportion of industries with high robot utilization, such as electric, electronic, chemical, and transportation equipment, in the Korean industry.

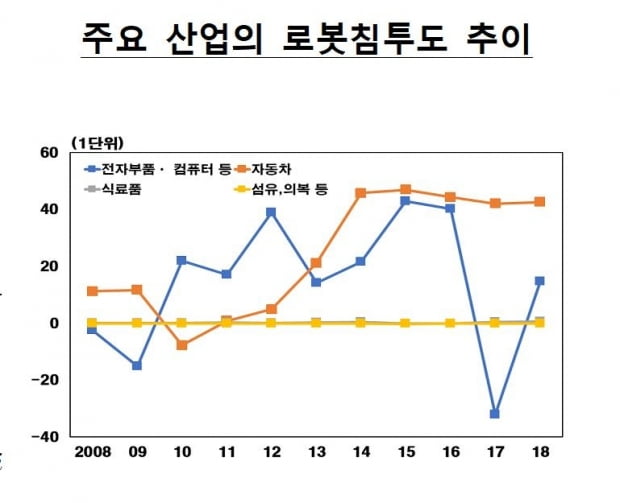
As a result of estimating the degree of’robot penetration’ by domestic industry, it was found that the distribution of robots is rapidly progressing, especially in the automobile, electronic parts, and computer industries.
The degree of penetration of robots refers to the gap between the actual increase in robot distribution per 1,000 people and the expected increase in the rate of increase in added value of the industry.
If the degree of penetration of the robot is greater than 0, it means that the speed of robot penetration is faster than the growth rate of added value of the industry.
In particular, the penetration of robots in the automobile business from 2010 to 2018 increased by 6.3 units on average per year.
From 2010 to 2016, the penetration of robots in the electronic parts and computer industries also increased by 3.05 units per year on average.
As a result of analyzing the relationship between robot penetration, the number of workers, and real wages by the BOK, if the robot penetration rate increases by 1 unit in an industry from 2010 to 2018, the increase rate of the number of workers is about 0.1% point (p), and the real wage increase rate is It is estimated that each decrease by about 0.3 percentage points.
In a report, Eun Eun said, “The role of robots will steadily expand along with technological advances and digital transformation after the novel coronavirus infection (Corona 19).” He advised that it is necessary to actively discover new high value-added industries and increase the’labor movement’ between sectors to continue.

/yunhap news