(Provided by Southern Branch = Ministry of Small and Medium Venture Business)
The Ministry of SMEs and Startups is the’Technology-based Venture and Startup Complex Financing Plan’, which includes the introduction of Silicon Valley-style investment conditional loans at the 26th Emergency Economy Central Countermeasure Headquarters Meeting and the 9th Korean New Deal Ministers’ Meeting. ‘Was announced on the 13th.
The plan is to create a complex financial system that combines technology development (R&D)-investment-guarantee-financing to support 3 trillion won by 2022 and create more than 20,000 jobs.
As of 2019, venture investment of 4.3 trillion won (2 trillion won in the first venture boom in 2000), 120,000 newly established corporations in 2020 (estimated), 6th in the world number of unicorn companies, advancement of innovative venture companies in the listed market, etc. It is evaluated that Korea’s second venture boom has reached full scale.
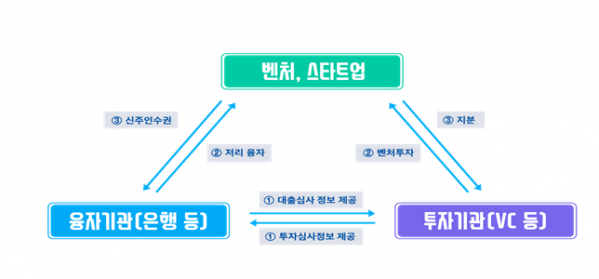
Due to the nature of start-ups and venture companies, it takes a long time to settle in the market, and there are many cases of difficulty in financing because there is no collateral other than intangible assets such as low creditworthiness and technology. From the perspective of lenders and guarantors, there is no choice but to feel the burden of lending to innovative companies with high risk of loss (high risk-low returns), and even when private investment institutions such as start-up investment companies are playing a role of supplying venture capital, blind spots such as non-metropolitan areas are occurring.
Accordingly, it was pointed out that a sophisticated customized policy is necessary to establish itself as one of the’four major venture powers’.
The government will create a customized complex financial system that combines technology development (R&D), investment, guarantee, and financing in consideration of the characteristics of technology-based start-ups and venture companies. The technology is excellent, but the introduction of a system that reduces the risk of funding institutions is the key to taking into account the characteristics of companies that involve high risks when providing funding.
It consists of 23 detailed implementation tasks for four strategies: △Introduction of the Silicon Valley-type compound finance system △Preparation of compound finance based on R&D project △Compensation of the gap in venture investment using compound finance △Four strategies to create a foundation for complex finance activation.
First, the government revised the Venture Investment Act to promote the introduction of the’Silicon Valley Conditional Investment Loan’ system in Korea.
The conditional investment loan is a system in which a lender receives a small amount of equity acquisition rights instead of giving low-interest loans to companies that have already received venture investment and are likely to invest further.
U.S. conditional loans amounted to $12.63 billion (estimated) in 2017, accounting for 15% of all U.S. venture investments. Silicon Valley Bank, a leading U.S. loan conditional financing institution, usually acquires the right to acquire shares of about 1-2% of the loan amount.
From the standpoint of lenders, loans to companies with high potential for follow-up investment increase the possibility of recovery, and through the right to take over shares, the company can earn higher than the interest rate when the company grows.
From the perspective of a company, it is possible to increase the possibility of subsequent investment while growing the company by receiving a loan, and because it is a loan rather than an investment, it is possible to prevent the diluting of the equity of the founder, etc.
After the revision of the law, the Ministry of SMEs will conduct a pilot operation through a policy loan from the Small and Medium Venture Business Corporation, and plan to spread it to other public funds and private financial institutions in the future.
Prior to the revision of the law, the Technology Guarantee Fund, which has an effect similar to that of an investment conditional loan, will be expanded to an annual scale of 200 billion won. In particular, a new’Patent (IP) Investment Option Guarantee’, which converts part of the guarantee amount into a patent (IP) share (repayment of loan) is also introduced.
Similar to investment conditional financing, the guarantee institution can convert part of the deposit amount into the equity of the company subject to guarantee, and the investment option guarantee is based on the ownership interest of the patent (IP) rather than the corporate equity. Switch.
In addition, to promote venture investment and diversify investment methods for early start-ups, the’Convertible Note’ system used in Silicon Valley, etc. will be introduced.
The’Contingent Equity Conversion Contract’ is a contract that receives principal and interest during the investment period if subsequent investment is not carried out, and issues convertible bonds under the commercial law when subsequent investment is carried out. It is an investment method of Silicon Valley that is commonly used for early start-ups as it has the advantage that the corporate value is determined by subsequent investors.
The complex financial system to help commercialize government technology development projects is also expanded.
Establishment of’Project Unit Technology Development (R&D) Commercialization Financing’ at a scale of 500 billion won in 2021-2022, which evaluates the possibility of commercialization of technology development success projects without looking at the company’s existing debts, and supports both technology guarantee and commercialization fund loans. do.
In addition, investment-type technology development that links technology development and venture investment from 16.5 billion won last year to 33.5 billion won this year, and deferred payment technology development that links technology development and guarantees from 14.3 billion won to 21 billion won, a total of 30.8 billion won. It will be expanded to 54.5 billion won.
In addition, the’carbon value evaluation-based Green New Deal Guarantee’, which supports finance by evaluating the amount of GHG reduction in green technology development projects in currency units, will also be implemented in earnest from this year. It is expected to be provided in an annual amount of 450 billion won through cooperation between the Ministry of Industry and the Small and Medium Enterprises, including contributions to the Technology Guarantee Fund of the Electric Power Industry Infrastructure Fund.
The complex financial system will also be reinforced to compensate for the blind spot of venture investment.
First, a guarantee system for startup investment companies is introduced. In order to form venture funds, start-up investment companies have usually invested about 10% of the funds formed in the fund. However, since venture funds are operated for a long period of time for 7 to 10 years, there have been many cases of difficulty in quickly forming funds due to temporary liquidity issues when forming additional funds in addition to the existing funds.
For the prompt formation and execution of venture funds, we plan to provide guarantees to secure temporary capital.
In addition, the venture investment capacity of public institutions is focused on non-metropolitan companies. Kibo is currently unable to invest in companies invested by the parental fund, but plans to make investments in non-metropolitan companies among the parental fund investment companies.
The current 45% of non-metropolitan companies’ investment share will also be operated so that by 2025 it is more than 65% of the annual investment.
For companies that are experiencing temporary difficulties due to Corona 19 or located in non-metropolitan areas, up to 500 billion won will be raised and invested in the four areas of the’Stretch Fund’ and the’Local New Deal Venture Fund’.
The’Support Fund’ will be invested in concerts with reduced face-to-face opportunities, travel and tourism, wholesale and retail, and companies with reduced exports, and the’Regional New Deal Venture Fund’ will be expanded for each region after a pilot is established in Busan.
Finally, we will build the foundation for the ecosystem so that the new complex financial institutions can operate smoothly.
In order to resolve information asymmetry between companies and investors and to quickly invest in technology companies, corporate data held by public institutions is converted into big data, and the’venture investment artificial intelligence online matching platform (tentative name)’ will be established by 2022.
This allows companies and investors to explore and connect investment possibilities.
Two local angel investment hubs will be established this year to revitalize the initial investment of non-metropolitan companies, and the company plans to induce investment expansion through a matching program with investors.
Minister of the Middle and Medium Industry Park Young-seon said, “Amid Corona 19, ventures and unicorns emerge as the leading roles of the KOSPI 3000-KOSDAQ 1000 and play a role in supporting the Korean economy.” “So that the fever of the second venture boom does not fade. “We will ensure that innovative ventures and start-ups will become the new leading players in the Korean economy and the support for creating jobs by implementing the’complex finance tailored to technology start-ups and venture companies’ without a hitch.”