Smart City Service Significantly expanded from 18 locations last year to 44 locations
City Challenge 4 preliminary projects and 2 main projects selected
Campus Challenge 9 universities selected, up to 1.5 billion won for 2 years
As a solution business, it is distributed to 22 locations of 9 major services
The number of new areas for the smart challenge project in which local governments and the private sector work together to discover smart city services will increase significantly from 18 to 44 last year. In addition to the existing projects, a total of 155.5 billion won was provided, and the’Campus Challenge’ project was also established, which allows universities to experiment with services.
The Ministry of Land, Infrastructure and Transport announced that the 2021 Smart Challenge project will be held on the 12th.

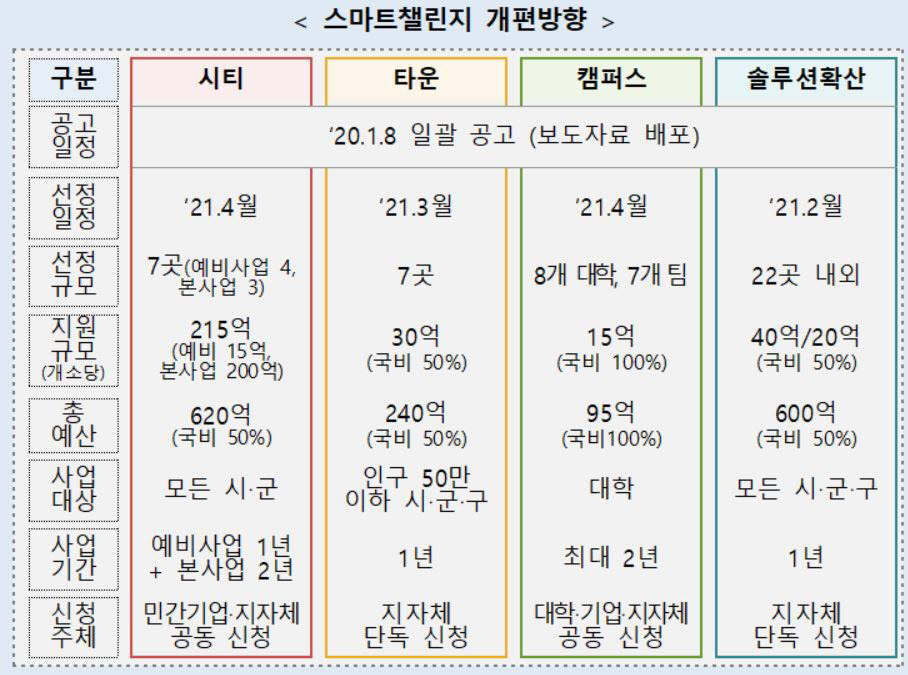
The smart challenge project consists of △ a smart city that demonstrates a comprehensive solution across the city △ a smart town specialized in small and medium-sized cities, △ a campus challenge that discovers ideas based on research and development achievements at universities, and △ 9 service solutions diffusion projects.
The City Challenge, which introduces and demonstrates smart city services across the city, consists of a preliminary project and a main project. In the preliminary project, government funds of 1.5 billion won each are invested in four cities to support the establishment of a master plan and pilot projects. Among them, two of them with excellent performance are selected as the main project and supported by 20 billion won (50% of government expenses) for two years.
Local governments running the City Challenge project are planning to establish a’Smart City Plan’ that implements various smart services such as transportation, environment, and energy in urban spaces to promote smartization across the city.
The Town Challenge specialized for small and medium-sized cities is a business that applies solutions optimized for small and medium-sized cities. Typical examples are the installation of an air quality meter at subway stations and a smart crosswalk. The competition target is limited to cities, counties and districts with a population of 500,000 or less. A total of 4 locations will be selected and proceed with a scale of 3 billion won (50% of the government expenses) per year.
Starting this year, the’Campus Challenge’ will be introduced, in which companies and local governments experiment with and commercialize smart services in the region, centering on universities. A total of eight universities will be selected in two fields: a research subject-linked type that utilizes the university’s R&D and intellectual property rights, and a community-connected type that tests services using various public information. It supports up to KRW 1.5 billion over two years.
Separately, an idea contest is also held in which university students are offered solutions for smart city implementation. Seven teams are selected to support 100 million won per team.
This year, the’Smart Solution Spreading Business’ will be greatly expanded so that the citizens can experience smart city services by distributing smart solutions with proven effectiveness nationwide.
From last year’s 10 locations, this year’s distribution will be doubled to around 22 locations. The scale of the project is also expected to increase significantly from 600 million won per city to 2 to 4 billion won (50% of national expenditure).
Nine services will be selected and distributed, focusing on solutions related to transportation and safety that have proven excellence in the existing challenge business. It is promoted in a way that local governments can select and utilize solutions that are optimized to solve problems in each city.
△ A’Smart Crosswalk’ that includes information on pedestrian safety and vehicle stop line compliance △ A’Smart Pole’ that combines CCTV, Internet of Things (IoT) sensor, and Wi-Fi on streetlights △ Possible to link and operate public and private parking lots Typical examples include’shared parking’, a’demand-responsive bus’ that flexibly operates routes in real time according to traffic demand, and’autonomous navigation drones’ that can be used for disaster and accident detection and delivery to island areas.

A total of 44 locations will be selected through a first-stage evaluation (written) for the solution diffusion project after a 1–2 month application period for each challenge project, and a second-stage evaluation for the City/Town/Campus Challenge.
Meanwhile, for the preliminary project areas for the City Town Challenge selected last year, 6 main business areas (City 3, Town 3) will be decided through competition in February.
Im-Rak Choi, director of urban policy at the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, and Transport said, “We will focus on spreading smart city solutions nationwide so that the people can experience the effects of smart city evenly. In addition, we will find innovative services and commercialize them to further enhance the smart city industry ecosystem. I will focus on strengthening it.”

Moonbo Player [email protected]