 |
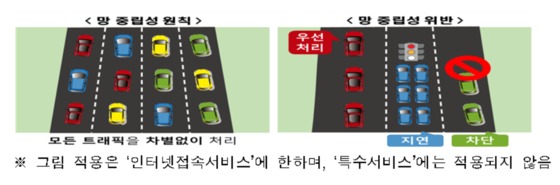
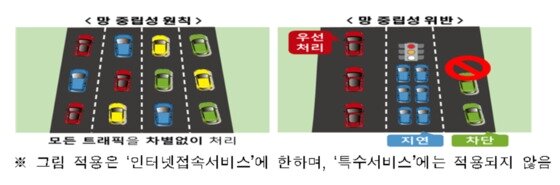
| Illustration of net neutrality. (Provided by the Ministry of Science and ICT/News 1) |
A new guideline for net neutrality has been established. It maintains the principle of network neutrality, but introduces the concept of’special service’ to clarify the network neutral exception service requirements. It is evaluated that it has laid the institutional foundation to activate new convergence services such as self-driving cars, which have been steadily approaching with the development of network technologies such as 5G, which has attracted attention as next-generation communication.
On the 27th, the Ministry of Science and Technology and Information and Communication announced that it has made an amendment to the’Guideline on Network Neutrality and Internet Traffic Management’ (Network Neutrality Guideline) that gathered opinions from various fields in order to respond to the development of network technology such as 5G mobile communication. .
Network neutrality is the principle that a telecommunications service provider (ISP) should treat legitimate Internet traffic equally regardless of its content, type, and provider. Since 2012, Korea has implemented the net neutrality guideline, which stipulates the main contents of the net neutrality principle.
However, with the recent development of network technologies such as 5G, communication service providers have been able to provide convergence services that require a certain quality, such as autonomous vehicles, and there is concern that the Internet quality used by general users may deteriorate in the process of spreading convergence services.
It has also been pointed out that the requirements for providing new convergence services are not clear under the current laws.
Accordingly, the Ministry of Science and ICT has formed and operated a network neutrality research group (Chairman, Professor Sung-Yup Lee, Korea University) from June 2019. The study group consisted of three telecom companies, content providers (CP, Kakao, Watcha, Korea Startup Forum), and experts in law, economy, and technology, and discussions were conducted in the first and second phases.
The amendment, which was prepared in 1 year and 6 months, was characterized by introducing the concept of special services such as overseas (EU, US) and meeting the needs of both communication and content providers, the Ministry of Science and ICT explained.
The Ministry of Science and ICT made it clear that “if the network neutrality principle is maintained and the requirements for provision of special services are met, new convergence services such as autonomous vehicles can be provided. In addition, it is meaningful that the communication service provider must provide relevant information transparently. “He explained.
“This is in line with global policy trends, such as the EU’s strict adherence to the net neutrality principle, while allowing the provision of special services under certain requirements, while the US Biden administration is expected to restore the net neutrality principle.”
According to the amendment, special services are provided for specific purposes by guaranteeing a certain quality level (speed, delay level, etc.) for △only specific users, but △services provided through separate networks separated physically or logically from Internet access services. Defined.
As a result, the evaluation that’there is uncertainty in the provision of new convergence services under network neutrality’ has been resolved, and services can be provided if these certain requirements are met even under network neutrality.
The conditions for providing special services were also specified. Telecommunications operators are prohibited from △maintaining an appropriate level of Internet access service quality, △continuously upgrading the network, and △providing special services for the purpose of avoiding the network neutrality principle.
This is to prevent the possibility of abuse of special services by communication service providers, such as keeping the Internet quality used by general users at an appropriate level even when special services are provided.
In addition, transparency has been strengthened to alleviate information asymmetry between users such as telecommunications and content providers. The revised bill △ expanded the subject of information disclosure by telecommunications companies, △ checked the quality of Internet access service, etc. △ allowed the telecommunications company to submit related data.
The Ministry of Science and ICT plans to implement the revised guidelines from January next year, prepare a commentary so that it can be applied smoothly in the field, and continuously monitor market conditions.
Through this, it is a policy to promote sound and sustainable development of the Internet ecosystem, and to continue policy efforts to ensure fair competition conditions and users’ rights among operators.