![(From left) Professor Lee Han-seok, Ph.D. Daegon Kim, and Sang-yoon Han [사진 출처=카이스트]](https://i0.wp.com/cdn.lecturernews.com/news/photo/202012/58191_223929_296.jpg?w=560&ssl=1)
[한국강사신문 한상형 기자] KAIST(President Sung-cheol Shin)Physics Department Lee Han-seok, Professor Yonghee Lee Joint Research Team(First Generation Collaboration Lab)Professor Moohan Choi, Kyungpook National University, Through joint research with Professor Deok-Yong Choi’s research team at Australian National University,·Low power·Low noise *He succeeded in implementing the Brillouin laser. 23Sun said. Ultra-compact with little frequency fluctuation·Low power·The low-noise light source is a key element required for the construction of the next-generation ultra-precision optical sensor..
☞ Brillouin laser(Brillouin laser): *Generates and amplifies laser light based on Brillouin scattering,, So the easier the laser’s medium produces Brillouin scattering, the less energy it can operate.. The output laser light has a lower frequency fluctuation and very low noise than the input pump light..
☞ Brillouin scattering(Brillouin scattering): Sound waves through light interacting with the medium(acoustic phonon)The phenomenon of generating and scattering. The scattered light undergoes a frequency reduction corresponding to the energy of the sound wave, Induced emission(stimulated emission) In other words, it is possible to duplicate light of the same characteristics, so it can be used in laser construction..
The joint research team maximized the performance by developing a Brillouin laser based on a chalcogen compound glass, where Brillouin scattering occurs hundreds of times better than conventional materials.. Chalcogen compound glass has a fundamental weakness that it is difficult to form by etching on a chip due to chemical instability, but the research team solved this problem by developing a new fabrication technique in which an optical element is spontaneously formed during the deposition process.
The manufacturing technique developed by the research team can be compared to obtaining the desired shape of snow by controlling only the shape of the roof without directly touching the snow, since the shape of the snow accumulated on the roof in winter is determined by the shape of the roof.. In other words, If the floor structure is properly formed using silicon oxide, which is easy to process with the current semiconductor process technology,, This is the first proof of the phenomenon of spontaneous formation of high-performance optical devices just by depositing chalcogen compound glass on top of it..
The joint research team succeeded in implementing a high-performance Brillouin laser based on a chalcogen compound glass in the form of a microscopic optical device on a semiconductor chip using this self-developed manufacturing technique.. Also, than the previous record 100It was revealed that the laser can be driven with more than twice the energy of the pump..
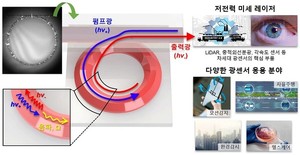
The official of the joint research team “Miniaturization and low-power driving are essential factors for commercializationˮSaying “The joint research team’s development of the Brillouin laser light source is expected to be widely used in the development of next-generation optical sensors, such as dramatically improving the sensitivity of the rotational inertia sensor as well as the distance required for autonomous driving.ˮSaid.
He also “The new process technique developed in the research process introduces various materials that could not be used so far into the field of microscopic optical devices., It is not only very meaningful in that it has made it possible, but it is also a source technology that is likely to be widely used in the future.ˮWas given meaning.
![Figure 1. Introduction of the fabrication principle, driving principle and application fields of the implemented ultra-compact, low-power Brillouin laser [사진 출처=카이스트]](https://i0.wp.com/cdn.lecturernews.com/news/photo/202012/58191_223930_2917.jpg?w=560&ssl=1)
Corresponding author, Professor Han-Seok Lee, who led this study “Chalcogen compound glass can be applied to the mid-infrared band where absorption lines of various molecules exist, so it will be able to expand its application range to the field of environmental monitoring and healthcare based on molecular spectroscopy.ˮI predicted. Another corresponding author, Professor Deok-Yong Choi, “The process technique developed in the research process is a heterogeneous combination of various substances(hybrid integration)It can be applied to the field of high-efficiency quantum light sources and quantum memory, which are the key devices of the future quantum internet.ˮEmphasized.
KAIST Physics Dept. Kim Dae-Gon PhD student and Han Sang-yoon Postdoctoral Fellow(Present Daegu Gyeongbuk Institute of Science and Technology Professor)This joint articleOne This paper by the joint research team who participated as an author is an international journal `Nature Communications(Nature Communications)’ 11month 23Work 字Featured on. (Thesis name: Universal light-guiding geometry for on-chip resonators having extremely high Q-factor)
Meanwhile, this study 2018It was selected for the Samsung Future Technology Promotion Project in 2012 and was carried out with continuous support..