|
Corporate performance evaluation due to corona, practically impossible
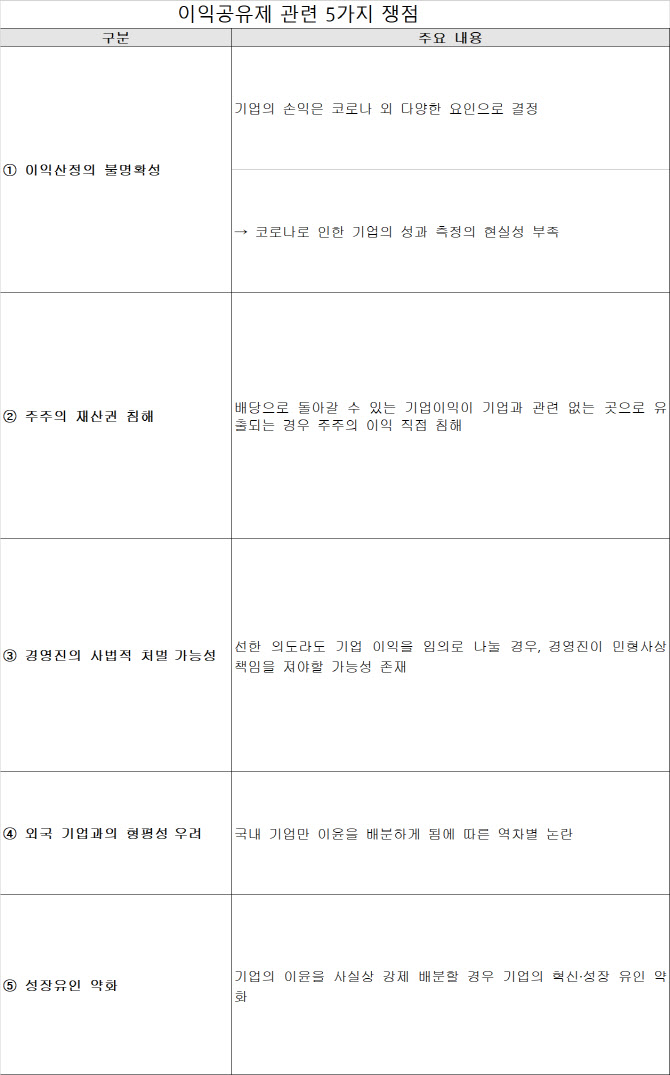
The FKI announced on the 17th that the introduction of the profit-sharing system does not make sense in a report entitled’Five Issues of the Profit-Sharing System’. First, the FKI argued that the calculation of profits was unclear. The justification of the corona benefit-sharing system starts from the assumption that the increase in profits due to the corona is clear, but it is said that it is virtually impossible to obtain the results of companies caused by the corona.
In addition to the situation of Corona 19, corporate profits and losses are determined by various factors such as global economy, product competitiveness, corporate marketing capabilities, market trend changes, business conditions, and exchange rates, the FKI explained.
FKI officials said, “As the target of profit sharing, platform and non-face-to-face companies such as △ semiconductor and home appliance conglomerates △ Kakao △ delivery people, etc. are being discussed. If the research and development were not preceded, the competition would have been eliminated before benefiting from the coronavirus.”
“In the case of Korea’s leading information technology (IT) companies, even if sales are negative, the rate of increase in R&D investment is steadily maintained at a high level.” It cannot be explained without the fact that the distribution trend has accelerated. In addition, to stabilize the platform, it is not appropriate to discuss the special coronavirus while ignoring the period of sustained investments and taking a deficit.”
Possibility of applying the system only to domestic companies, not foreign companies
The FKI emphasized that the benefit-sharing system could infringe shareholders’ property rights. Based on the Win-Win Cooperation Act, the performance-sharing system, widely implemented by large companies, is a system that shares the results of joint cooperation between large companies and partner companies, such as new product development, productivity improvement, and cost reduction. On the other hand, the benefit-sharing system is a concept of sharing the profits of large, non-face-to-face, and platform companies that benefit from Corona 19 to small and medium-sized businesses and small business owners who are suffering damage.
In a capitalist society, shareholders are the claimants for the residual income from business activities, that is, the entity who can get the remaining net profit after paying a fair price for the inputs required for production. The FKI pointed out that if some of the corporate profits that can be returned as dividends are returned to companies or small business owners that are not related to the company, the problem of directly infringing the interests of shareholders occurs.
In addition, the FKI argued that a company’s litigation risk could additionally increase with the introduction of a number of systems that make it difficult for companies to manage smoothly, such as the multiple representative lawsuit system and strengthening minority shareholder rights.
In addition, the FKI is concerned with the possibility of judicial punishment by management that could expose the management to civil and criminal responsibilities if the company’s interests are arbitrarily shared △Equity concerns that the profit-sharing system can be applied only to domestic companies, not foreign companies such as Netflix. △ He pointed out the problems of the profit-sharing system, such as weakening growth incentives that can weaken corporate profit-seeking and innovation incentives.