Could the’dog that doesn’t bark’ be different? The voice of anticipation of the return of inflation that has disappeared is empowering. Despite the liquidity that is overflowing in the market due to zero interest rates and stimulus measures from each country, the prices did not budge like rocks. That’s why the International Monetary Fund (IMF) said in its 2013 report that’the price is like a dog that doesn’t bark’.
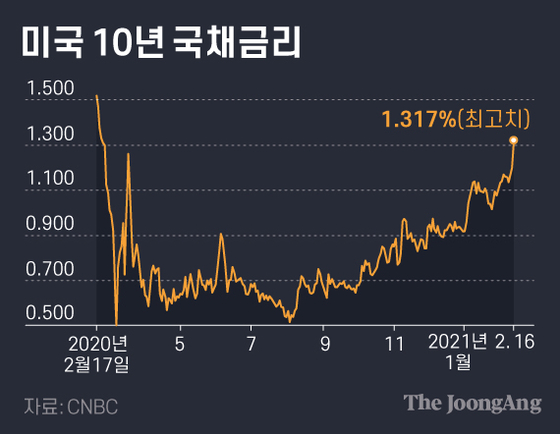
A signal that sensitively sensed the signs of inflation that had disappeared rang. U.S. Treasury yields are shaking. The US 10-year Treasury bond yield, which hit a historic low (0.51%) in August last year, rose to 1.317% during the intraday on the 16th (local time).

US 10-year Treasury yield. Graphic = Kim Eun-kyo [email protected]
The rise in international oil prices amid strong raw materials has boosted government bond yields. Western Texas Crude Oil (WTI) for delivery in March was traded at $60.05 per barrel, the highest in one year and one month. It rose by 23.76% in a month and a half. The market was shaken. The stock market fell on this day.
Treasury bond yields have risen sharply, rekindling the inflation debate. The representative predictor of the return of inflation is Larry Summers, a professor at Harvard University. Summers, who served as Treasury Secretary for the Bill Clinton administration and Chairman of the White House National Economy Committee for the Barack Obama administration, said in a column in the Washington Post (WP) on the 5th, “A massive stimulus package equivalent to World War II will cause inflationary pressures not experienced within a generation I can do it,” he warned.
There are several reasons for predicting the return of inflation. It is argued that prices are rising due to the enormous liquidity poured out by governments to prevent the economic downturn caused by the novel coronavirus infection (Corona 19). It is the theory of quantity of money.
Jeremy Segal, a professor at the University of Pennsylvania’s Wharton School, told the Financial Times (FT), “Liquidity is flowing into the real economy, which increases inflation pressure.” “The current situation is different from QE at the time of the 2008 global financial crisis.” Pointed out. In 2008, as the released liquidity was absorbed into the bank’s excess payment reserves, there was no real money in the market, but now, the liquidity is overflowing due to the government’s dispensing money through cash payments.
The central bank’s stance, which has transformed from a’inflation fighter’ to a’job fighter’, is also a factor inspiring inflation. In a situation where the labor market situation has deteriorated due to Corona 19, etc., it has no choice but to tolerate an increase in inflation because it has no choice but to continue a easing monetary policy for the time being. Some analysts say that there will also be concerns that a premature increase in interest rates and the like, which may put a cold water on the economic recovery trend, will also act.
There are also views that inflation can be used to reduce the burden of growing debt. “Inflation is the easiest way to resolve government debt without resistance,” said Song Ki-jong, head of NICE Credit Ratings Financial Evaluation Division 3, in the report, “The return of inflation and the possibility of long-term interest rates rise”.
Changes in the demographic structure of emerging economies such as China, which enabled low prices, and the decline of globalization could also stimulate the return of inflation. Professor Charles Goodheart of the London School of Economics and Economics is the leading player who makes this claim. Professor Goodheart predicts that the’low price-low interest rate’ keynote will change into a new era of’high price price-high interest rate’ due to the aging population structure and the decline of globalization.

Western Texas Oil (WTI) price trend. Graphic = Kim Eun-kyo [email protected]
In addition, the possibility of supply-driven inflation is raised as economic activity, which had been contracted by Corona 19, resumes. If production disruptions occur and suppressed demand explodes, product and service prices will inevitably rise. Kim Il-koo, chief economist at Hanwha Financial Investment, said in the report, “In the 3rd to 4th quarter of this year, we expect to experience a sudden increase in inflation due to rising raw material prices and service prices.”
The objection is also difficult. It is not easy for inflation to set foot again in a situation where low interest rates have been fixed. This is why the Federal Reserve System (Fed) emphasizes that inflation is manageable.
First of all, it is a view that overflowing idle manpower and idle facilities can hinder inflation. JPMorgan pointed out that “the supply disruption caused by Corona 19 is a short-term factor, and idle resources lead to inflationary pressure, and even in the situation of full employment before Corona 19, the inflation rate target (2%) was not achieved.”
In addition, some analyzes say that changes in the labor structure cannot be a factor that will lead to wage-driven inflation. “There is also a phenomenon in progress that the demand for low-skilled labor is decreasing due to technological advancement,” said Song. As can be seen in the case of Japan’s’Abenomics’, some argue that fiscal expenditure and extreme monetary easing policies do not lead to a surge in inflation.

Major investment banks (IBs) forecast US inflation. Major investment banks (IB) forecast for inflation in the US
The market’s concern over the return of inflation is monetary tightening due to inflation. It is the fear of the shock when the liquidity flowing out of the market is dry. It is the so-called’tapering tentrum’ that shocked the market in 2013, long after the global financial crisis. Due to the base effect, the US inflation rate is expected to approach 2.5% this year, exceeding the Fed’s target of 2%.
However, it is unlikely that the Fed will be quick to pull out a rate hike card. This is because the company has declared an average price target (AIT) and is expected to tolerate inflation overshooting (rising above the appropriate level) for the time being. The British Economist also pointed out that “the Fed wants inflation above a certain level to fill the past inflation shortfall.”
The market predicts that it is more likely to take other measures than to raise interest rates to prevent a surge in inflation. This is because there is a concern that it will cause an economic downturn due to an interest rate hike. Societe Generale said, “The Fed will not pay much attention to the rise in long-term interest rates.” “If interest rates rise rapidly and steeply in the future, there is a possibility of utilizing the’operation twist’ (selling short-term bonds and buying long-term bonds to flatten bond yields). It is big.”
Reporter Ha Hyun-ok [email protected]